The 4 Aspects
V • Volition
L • Logic
F • Physics
E • Expression
Blocks
V+L • F+E
V+F • L+E
V+E • L+F
Attitude Valence
The 4 Positions
Confident
Flexible
Insecure
Unbothered
Position Pairs
Self-focused
Others-focused
Method-focused
The 6 Functions
Function 1 & 6
Function 2 & 5
Function 3 & 4
The 16 Attitudes
Confident Attitudes
1V • 1L • 1F • 1E
Flexible Attitudes
2V • 2L • 2F • 2E
Insecure Attitudes
3V • 3L • 3F • 3E
Disowned Attitudes
4V • 4L • 4F • 4E
Subtypes
Subtypes Cheatsheet
Basic Theory
The 4 Aspects
Attitudinal Psyche is a personality system which theorizes that all individuals have a set structure of fundamental attitudes that creates unique dispositions towards four main aspects of life: Physics (F), Expression (E), Logic (L), and Volition (V).
Physics - "F"
Physics (also referred to as “Foundation” or “Feelings”) is the aspect that reigns over the human experience of sensual perception, feelings, physical matter, materials, environments, bodily sensations, appearances, aesthetics, possessions, comforts, and instinctual awareness of all stimuli.
Expression - "E"
Expression (formerly known as “Emotion”) is the aspect that reigns over the human ability to judge who or what you find subjectively better versus worse, evaluate the worth of people and relationships, give meaning and sentimental value to what happens to you, rank things on a hierarchy of most liked to disliked, and to decide how you believe the scale of moral versus immoral should be organized.
Logic - "L"
Logic is the aspect that reigns over the human ability to evaluate statistical categories, assign numerical values, reason out facts, compare and contrast data, prove what is true or false, and judge whether something is factually correct or incorrect.
Volition - "V"
Volition is the aspect that reigns over the human experience of causality, the personality, time, pathways, intuitive perception, future desires, making plans, imagining a direction, reading power dynamics/character/identity/themes, and perceiving a projection of possible past or future realities.
Blocks
The four main aspects can be combined into pairs and then contrasted against one another. We call these “blocks” and understanding where each falls in a core type offers an extremely refined understanding of how that type operates.
Strategist (V+L) vs. Reactivist (F+E)
Volition & Logic (Strategist)
The strategist pole of this dichotomy is the traditional “yang” energy that both volition and logic hold within them. Volition is all about projections, imagining a direction, and expanding one’s power to incorporate more options or ideas within the causality of time. Likewise, the logic aspect is related to volition because it too reigns over an expansive view of how things relate to other things in a way that can be given a designated numerical or statistical value. Logic is assigning truth value to objects which means determining or assessing the measurement of that thing. Combine these two aspects together and you create all elements needed to become an expert chess player: strategy, tactics, schemes, pattern creations, power moves, projections, and logical calculations.
Physics & Expression (Reactivist)
The reactivist pole of this dichotomy is the traditional “yin” energy that both physics and expression hold within them. Physics is about raw perceptions and responses to sensations, the body, and how one experiences the world happening to them. Expression relates to the subjective value we give to what happens to us, therefore it’s technically a response to reality despite it being a subjective judgment. Combine these two aspects together and you create all components needed to become a skilled mood evaluator: aesthetic discernment, emotional impact, taste, affinity, fondness, penchants, reactions and awareness of how the environment can affect your likes and dislikes.
Experiencer (V+F) vs. Evaluator (L+E)
Volition & Physics (Experiencer)
The experiencer pole of this dichotomy is how volition and physics relate to one another through their intrinsic experience of observation through both real and projected realities. This drive can be felt internally by the individual and seen externally by others. Both volition and physics are often seen through perceptions and instincts rather than words or values. Volition relates to projecting future pathways and imagining how one could act. Physics relates to raw sensual feelings and perceiving the world through the body. Combine these aspects together and you create all elements needed to become a go-getter: maneuvering, realizing potential, raw perception, sense of self, environmental awareness, and an active observation of how objects can be manipulated to fulfill future objectives.
Logic & Expression (Evaluator)
The evaluator pole of this dichotomy is how logic and expression relate to one another through their need to assign value to things. Both aspects tend to be verbal in nature, so language and communication is the easiest way to see them in action. Logic is assigning numerical value in order to evaluate truth. Expression is assigning subjective value in order to evaluate affinity. Combine these aspects together and you create all elements needed to become an expert appraiser: evaluations, judgments, labels, values, verbal assessments, opinions, and verdicts on how to designate merit to anything.
Conceptualist (V+E) vs. Realist (L+F)
Volition & Expression (Conceptualist)
The conceptualist pole of this dichotomy relates to the higher order of human attitudes or how one subjectively evaluates their affinity to time, identities, power, relationships, religions, politics, imagination or any other conceptual idea that aligns more with the abstract realm rather than what we can point to as taking up actual space in reality. This dichotomy is not necessarily about anything religious, but rather the value of the human spirit itself. Volition is perceiving intuitive projections of the past and future and what decisions change the causality of time. Expression is evaluating the subjective meaning of all things regardless of their physical existence. Combine these aspects together and you create all elements needed to become an idealist: visions, dreams, notions, fantasies, reveries, motivations, inspirations, and the drive to conceptualize meaning beyond what currently exists.
Logic & Physics (Realist)
The realist pole of this dichotomy relates to the more fundamental and foundational part of existence through objects, sensations, feelings and how they can be measured. All things in the environment can be felt or experienced, while also being given a specific measurement. One might ask the question “how happy are you?” in response to someone claiming a current state of happiness – which can be answered in a multitude of ways. One may also inquire the measurements of a new window needed for their home – but is it measured in metric, imperial, or a system unique to windows? Both circumstances are rooted in a real sense of what exists around us and how things can be categorized in numerous different ways. Combining these elements makes it possible to become an expert pragmatist: measurements, facts, actualities, magnitudes, truth layers, sensual perceptions, tangibles, and tactile experiences that create the stage in which life can be lived.
Attitude Valence
Attitude valence is the psychological concept of having positive or negative associations, reactions, or feelings towards an object, concept, idea, conclusion, ability, or judgment. In Attitudinal Psyche, we use valence to describe an overall pattern of negative or positive valence towards an aspect when either engaging in it personally, or reacting to how others are engaging with that aspect personally.
Self-Positive & Self-Negative Valence (S+ & S-)
Self-positive valence is an overall pattern of positive reactions, feelings, and associations towards the aspect being engaged. These positive reactions can range through a multitude of emotions: happiness, desire, pleasantness, enjoyment, confidence, reward-seeking, excitement, bliss, self-assuredness, acceptance, etc.
Self-negative valence is an overall pattern of negative reactions, feelings, and associations towards the aspect being engaged. These negative reactions can range through a multitude of emotions: displeasure, unhappiness, aversion, avoidance, disgust, fear, anxiety, loss, frustration, annoyance, rage, etc.
The 1st & 2nd positions are self-positive.
The 3rd & 4th positions are self-negative.
Others-Positive & Others-Negative Valence (O+ & O-)
The others attitudes are based on reactions to other people’s self-oriented valence. This means that you are building your positive or negative valence in response to the reactions that others are having to that aspect. In easier to understand terms: everyone is doing self attitudes and we are noticing and having reactions to one another by simply being social creatures, which is what creates the others attitude.
The 2nd & 4th positions are others-positive.
The 1st & 3rd positions are others-negative.
Personal & Impersonal Valence (S/O & P/R)
Not only can we have a positive or negative reaction to the aspects, but we can also switch between a personal & impersonal valence. An alternative word for impersonal could be described as neutral. A valence becomes neutral when you focus on the transfer of information between the self & others. If both valences match, the method becomes process-oriented which focuses on impersonal processing, discussing, handling, refining, and journeying through the aspect. If both valences do not match, the method becomes results-oriented which focuses on impersonal concluding, completing, finishing, determining and finalizing data within the aspect. A personal valence will always be focused on people’s reactions over the informational exchange. Everyone does both, though subtypes can reflect whether certain individuals have a preference towards one over the other in particular aspects.
The 1st & 4th positions are results-oriented.
The 2nd & 3rd positions are process-oriented.
Any focus on people (self, others or both) is personal.
Any focus on the exchange of information between self & others is impersonal.
The 4 Positions
There are four positions in Attitudinal Psyche. Each position expresses a positive or negative valence towards the self and others. These two valences are what come together in combination with the aspect held within to form a holistic portrayal of one’s overall attitude towards that aspect. Another way to look at each position is to imagine it as an energy that is perceived in a particular way.
1st: Hoarding the aspect for yourself. A one-way street of energy into the self and you are the conductor. “I take what I want from the world in relation to the aspect as this is my greatest gift.”
2nd: “Surfing” the aspect. The energy is available at all times and can be repeatedly crashed into the shore (other people). “I’m riding this wave until it crashes, then we repeat the cycle!”
3rd: Maneuvering through the dangers of the aspect in hypervigilance. The energy is violent and happening to you or around you without your consent. “I cannot control the aspect naturally unless I pay extreme attention to processing it.”
4th: Giving the aspect away – disowning it – expecting others to deal with it. The energy is leaving/evaporating/being given away, and therefore moving away from the self. “I give away the aspect to the world. I refuse to process it myself unless it is imperative to my survival, then I’ll get my answer and move on.”
Confident - 1st Position
Overview: Self-Positive (Energizing), Others-Negative (Defensive/Vulnerable), Results-Oriented (Distinct Outcome)
The first position is what we hold closest to our chests as it feels like it was birthed from our very existence. At an early age we merge with the aspect which creates an ever-present belief that it must be protected at all costs. No one can come around touching and contaminating the way that we interact with our own perceived greatest gift, and if you thought that was narcissistic, wait until you back someone’s 1st aspect into a corner! Not only does it feel worth protecting but it energizes us to give a sense of aliveness in the fight against decay, entropy and meaninglessness – or as I call it: the accelerating carnival ride towards death. When nothing else in the outside world can be counted on you still have yourself, and coincidentally we often believe the first aspect and ourselves are one and the same. The good news is this means it can never be lost. The bad news is others (as unintended as it may be) will still try to snag a piece of it.
Flexible - 2nd Position
Overview: Self-Positive (Energizing), Others-Positive (Calm/Fearless), Process-Oriented (Ongoing Narrative)
The second position is the aspect we freely process with anyone whether they want to hear about it or not. We’ve all had an experience with an over-sharer, whether it be in the line at the grocery store or an old friend who has way too much to say about whatever is going on in their life. This is among the same vein of how the second position operates. It’s entirely open, fearless, and willing to share whatever story is currently bubbling up regarding the aspect. Just because this position has a rather positive association in nomenclature does not mean it avoids mishaps. Like the person who has trapped you in an hour long conversation about the thing you don’t care about, this position can be overly eager to involve you in their problems, or even worse, implore you to share your own. Of course, subtypes can alter the way it presents itself but the initial reaction will always be to openly stir up some energy and hubbub around the aspect.
Insecure - 3rd Position
Overview: Self-Negative (Taxing), Others-Negative (Defensive/Vulnerable), Process-Oriented (Ongoing Narrative)
The third position is what I lovingly refer to as the PITA (pain in the ass). Directly tied to the ego, it has an ongoing fearful story of how the aspect could utterly destroy you. For this reason, the third position is hypervigilant about every single piece of information involved in the aspect, which means it’s looking sideways at itself and any unlucky individual who steps on the haphazardly placed landmine. Unfortunately, fires burn out quickly and the same can be said for this position. This is the most erratic of the four and often feels like an out-of-control, energy-taxing experience if you continue looking in its direction. Of course, not everyone keeps looking at what terrifies them and will instead place it on the backburner like a box of old, dirty, worn-out clothes hidden in the attic. But alas, this will not stop it from rearing its ugly head in your perception as soon as life inevitably throws situations at you that involve the aspect. The good news is individuals are relatively accepting of processing the aspect so long as it feels safe to do so, unlike its self-negative neighbor: the fourth position. The third position feels like a life long struggle that needs constant management and updates to the ongoing narrative you have of it in your mind.
Disowned - 4th Position
Overview: Self-Negative (Taxing), Others-Positive (Calm/Fearless), Results-Oriented (Distinct Outcome)
The fourth position is equivalent to the human appendix. Do we know if we need it? Not really. Can we take it out and never bother to worry about it again? Yes. Can it kill you if it gets infected and starts dissolving you from the inside out? Also yes. Much like appendixes (is that a word?), the fourth position is initially and consciously seen as useless to the self and can be an ongoing blind-spot to the individual who possesses it. Like the third position, thinking too much about the aspect feels taxing, energy depleting, and downright pointless. However, it’s not something that causes conscious terror nor does it feel like it’s important enough to be processed (whiny baby third position: take notes). Unfortunately for you, it does need processed, which means the longer you let it fester in your unconscious, the bigger the meltdown will be when you’re forced to deal with it. We often want quick answers and solutions for the aspect from others, which can lead to over-dependence on outside opinions and responsibility. Unlike the third position, we neglect the 4th aspect and become careless about how it gets done as long as it’s someone else’s problem and we never have to hear another story about that [expletive] thing again! “Take my money, and all my problems while you’re at it!” – famous last words of some 4X, probably.
Position Pairs & Dichotomies
Each position forms a dyad with all other positions based on a shared valence. This dyad sits in a dichotomous relationship with the opposing dyad. These dichotomies form the basis of the functions.
Self-focused Pairs & Dichotomy
Self Positive, Xs+ (1st & 2nd Positions)
-Energizing
Believes that the aspect energizes them.
Believes that their initial opinions or ideas about the aspect are relevant, needed, and applicable.
Believes that they have the energy to deal with complex and complicated reactions and attitudes that they may have about the aspect.
Self Negative, Xs- (3rd & 4th Positions)
-Taxing
Believes that the aspect is taxing to deal with.
Believes that their initial opinions or ideas about the aspect are unrefined, lacking, and not applicable.
Believes that they do not have the energy to deal with complex and complicated reactions and attitudes that they may have about the aspect.
Others-focused Pairs & Dichotomy
Others Positive, Xo+ (2nd & 4th Positions)
-Calm/Fearless
Believes that others’ reactions to the aspect pose no real danger to themselves.
Believes that information related to the aspect should be shared freely.
Reacts calmly to inquiries about the aspect.
Others Negative, Xo- (1st & 3rd Positions)
-Defensive/Vulnerable
Believes that others’ reactions to the aspect are (or could become) a threat to the self.
Believes that the information related to the aspect should be guarded.
Reacts defensively to inquiries about the aspect.
Method-focused Pairs & Dichotomy
Results Oriented, Xr (1st & 4th Positions)
-Distinct Outcome
Believes that answers are the most important part of information related to the aspect.
Believes that adding extraneous information to the aspect with no outcome in mind is a waste of time.
Believes that each piece of information within the aspect speaks for itself and does not need to be compared or contrasted to other pieces of information.
Process Oriented, Xp (2nd & 3rd Positions)
-Ongoing Narrative
Believes that discussion and questioning are the most important ways to deal with information related to the aspect.
Believes that adding extra information from multiple sources helps build the narrative around the aspect.
Believes that information regarding the aspect can be compared, contrasted, and intertwined with no need to conclude an end point.
The 6 Functions
The functions are formed by combining a block with a position pair and can be contrasted against each other. These functions represent the most significant and observable behavioral patterns in humans. This is the cornerstone of typing others in Attitudinal Psyche. Each function is numbered from 1-6, indicating a hierarchy of how often you will see it activated in someone’s behaviors – 1 being the most. Subtypes can slightly affect the overall distribution but they will never alter from this specific order. Functions can only be compared in behavioral distribution against their opposites as all aspects are constantly active in the personality at varying levels.
General Behavioral Distribution:
1st = 90% • 6th = 10%
2nd = 75% • 5th = 25%
3rd = 60% • 4th = 40%
Function 1 & 6
Function 1: Lifeblood
1st + 2nd Attitude Block
The lifeblood function is the block that energizes you without limitation. Nearly as natural as breathing air, it’s hard to notice that you are automatically engaging in this function without hesitation. The 2nd attitude comes up with possibilities in the outside world, processes them, and offers the energy to the 1st attitude to consume and benefit from. Easily enmeshed with the function, you may feel as though the information is too obvious to care about since it doesn’t trigger you which can lead to inverted self-typing. However, comparing the 1st and 6th functions shows how diametrically opposed they are on this energetic pole, as up to 90% of your energy goes into the 1st leaving as little as 10% for your 6th.
Function 6: Burnout
3rd + 4th Attitude Block
The burnout function is the block that hemorrhages energy when it gets stuck in processing mode within you. Since dealing with this function doesn’t happen as often as the lifeblood function, it’s terribly noticeable when it crops up into conscious awareness. For this reason, you might think you deal with it more than you actually do and this can lead to an inverted self-typing. Feeling entirely burnt out quickly is the driving force of this block. The 6th function is quickly outsourced to the 1st function when activated, as something must re-fill the depleted energy once its been bulldozed through. Many people describe their 6th function’s block as something that appears out of nowhere and can’t be easily controlled, so spending time and energy dealing with it leads to burnout.
Function 2 & 5
Function 2: Security
1st + 3rd Attitude Block
The security function is the block that feels the most dangerous to ignore. Therefore, you may over-process it due to its perceived importance to avoid any traps that could be hiding in plain sight. The 2nd function enjoys taking control and protecting its conclusions from others. Other people are often seen as the problem, so the ego makes sure to build walls between the self and the outside world to prevent manipulation or sabotage of the information this function holds close to the chest. The 2nd supports the 1st function by identifying vulnerabilities that may inhibit the free flow of energy into the psyche.
Function 5: Haphazard
2nd + 4th Attitude Block
The haphazard function is freely given away to others and its importance to the safety of the self is often underestimated. The 5th function is treated as something that doesn’t need much attention or care which makes it vulnerable to suggestion. The problem is that the individual does not catch on to the vulnerability which leads to accidental activation of triggering events usually related to the 4th attitude. The good news is not much energy is spent on this block, though it’s noticeably more active than the 6th function. The bad news is that once the negative side of the block is triggered, it’s hard for the individual to come up with solutions unless they fully give up on the problem itself or ignore its need for maintenance.
Function 3 & 4
Function 3: Launch
1st + 4th Attitude Block
The launch function is what focuses on each and every decision one chooses to make in their day. These decisions can range from massively important like changing a job, to banal daily activities like choosing your outfit or what to eat for lunch. Either way, this function is responsible for concluding the things we do not wish to process – mainly things related to the 4th attitude. Despite this function having a slight edge in focus over the spin-out function, they are relatively balanced as humans tend to need a fair amount of processing information to function well. For this reason, the launch function is less active than the security and lifeblood functions.
Function 4: Spin-out
2nd + 3rd Attitude Block
The spin-out function is where one over-processes both the affect they have on the outside world, and the affect the outside world has on them. Often resulting in anxiety, this function has a tendency to continue searching for more information to either perceive or judge, depending on the aspects held within. The problem is that without the launch function active, you have nowhere to aim the information towards. For this reason, the lifeblood and security functions are usually activated once enough time has passed swirling around in all available information. The spin-out function is theoretically the easiest to see in conversation.
The 16 Attitudes
An Attitude is formed when we place an aspect into a position. There are 16 total Attitudes in Attitudinal Psyche. These are the cornerstones of the personality types.
1V: Confident Volition
The 1V attitude is characterized by a self-positive (Vs+), others-negative (Vo-) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is acutely aware of its own strengths within the realm of volition. 1Vs understand their own power within this aspect and generally want to protect it at all costs. All incoming volitional information from others must be pushed through the 1V’s subjective interpretation before it is accepted. The strategies that each 1V employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of subjective protection over what they believe is their greatest asset will be consistent and true for all 1Vs. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 1Vs. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 1V attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
1L: Confident Logic
The 1L attitude is characterized by a self-positive (Ls+), and others-negative (Lo-) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is acutely aware of its own strengths within the realm of logic. 1Ls understand their own power within this aspect and generally want to protect it at all costs. All incoming logical information from others must be pushed through the 1L’s subjective interpretation before it is accepted. The strategies that each 1L employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of subjective protection over what they believe is their greatest asset will be consistent and true for all 1Ls. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 1Ls. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 1L attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
1F: Confident Physics
The 1F attitude is characterized by a self-positive (Fs+), others-negative (Fo-) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is acutely aware of its own strengths within the realm of physics. 1Fs understand their own power within this aspect and generally want to protect it at all costs. All incoming physical information from others must be pushed through the 1F’s subjective interpretation before it is accepted. The strategies that each 1F employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of subjective protection over what they believe is their greatest asset will be consistent and true for all 1Fs. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 1Fs. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 1F attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
1E: Confident Expression
The 1E attitude is characterized by a self-positive (Es+), others-negative (Eo-) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is acutely aware of its own strengths within the realm of expression. 1Es understand their own power within this aspect and generally want to protect it at all costs. All incoming expressional information from others must be pushed through the 1E’s subjective interpretation before it is accepted. The strategies that each 1E employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of subjective protection over what they believe is their greatest asset will be consistent and true for all 1Es. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 1Es. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 1E attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
2V: Flexible Volition
The 2V attitude is characterized by a self-positive (Vs+) and others-positive (Vo+) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is acutely aware of how volitional information can be transferred between itself and the outside world in both directions. 2Vs understand the elasticity, usefulness, and creative element within this aspect and generally feel a sense of fearlessness in discussing or sharing information within this realm. The strategies that each 2V employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitudinal belief in objective, flexible communication will remain consistent for all 2Vs. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 2Vs. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 2V attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
2L: Flexible Logic
The 2L attitude is characterized by a self-positive (Ls+) and others-positive (Lo+) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is acutely aware of how logical information can be transferred between itself and the outside world in both directions. 2Ls understand the elasticity, usefulness, and creative element within this aspect and generally feel a sense of fearlessness in discussing or sharing information within this realm. The strategies that each 2L employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of objective, flexible communication will remain consistent for all 2Ls. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 2Ls. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 2L attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
2F: Flexible Physics
The 2F attitude is characterized by a self-positive (Fs+) and others-positive (Fo+) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is acutely aware of how physical information can be transferred between itself and the outside world in both directions. 2Fs understand the elasticity, usefulness, and creative element within this aspect and generally feel a sense of fearlessness in discussing or sharing information within this realm. The strategies that each 2F employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of objective, flexible communication will remain consistent for all 2Fs. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 2Fs. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 2F attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
2E: Flexible Expression
The 2E attitude is characterized by a self-positive (Es+) and others-positive (Eo+) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is acutely aware of how expressional information can be transferred between itself and the outside world in both directions. 2Es understand the elasticity, usefulness, and creative element within this aspect and generally feel a sense of fearlessness in discussing or sharing information within this realm. The strategies that each 2E employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of objective, flexible communication will remain consistent for all 2Es. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 2Es. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 2E attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
3V: Insecure Volition
The 3V attitude is characterized by a self-negative (Vs-) and others-negative (Vo-) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is plagued by an awareness of limitations, weakness, harm, negative consequences, and manipulation within the realm of volition. This awareness applies internally, externally, and within the exchange of information in the aspect. 3Vs have a keen sense of how they can be harmed by volition. The strategies that each 3V employs to deal with the insecurity may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of subjective vulnerability and insecurity will remain consistent for all 3Vs. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 3Vs. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 3V attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
3L: Insecure Logic
The 3L attitude is characterized by a self-negative (Ls-) and others-negative (Lo-) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is plagued by an awareness of limitations, weakness, harm, negative consequences, and manipulation within the realm of logic. This awareness applies internally, externally, and within the exchange of information in the aspect. 3Ls have a keen sense of how they can be harmed by logic. The strategies that each 3L employs to deal with the insecurity may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of subjective vulnerability and insecurity will remain consistent for all 3Ls. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 3Ls. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 3L attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
3F: Insecure Physics
The 3F attitude is characterized by a self-negative (Fs-) and others-negative (Fo-) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is plagued by an awareness of limitations, weakness, harm, negative consequences, and manipulation within the realm of physics. This awareness applies internally, externally, and within the exchange of information in the aspect. 3Fs have a keen sense of how they can be harmed by physics. The strategies that each 3F employs to deal with the insecurity may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of subjective vulnerability and insecurity will remain consistent for all 3Fs. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 3Fs. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 3F attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
3E: Insecure Expression
The 3E attitude is characterized by a self-negative (Es-) and others-negative (Eo-) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that is plagued by an awareness of limitations, weakness, harm, negative consequences, and manipulation within the realm of expression. This awareness applies internally, externally, and within the exchange of information in the aspect. 3Es have a keen sense of how they can be harmed by expression. The strategies that each 3E employs to deal with the insecurity may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of subjective vulnerability and insecurity will remain consistent for all 3Es. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 3Es. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 3E attitude.
Attitudinal Beliefs
Coming soon…
4V: Disowned Volition
The 4V attitude is characterized by a self-negative (Vs-) and others-positive (Vo+) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that disowns perceiving how the realm of volition may affect them. 4Vs come to an understanding that outside sources have a better grasp over the aspect. The 4V feels a sense of carelessness with generating its own volitional perceptions and intuitions, and generally desires quick conclusions when they are forced to produce observations in this realm. The strategies that each 4V employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of acceptance of outside responsibility over volition will be consistent and true for all 4Vs. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 4Vs. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 4V attitude.
• Expects others to generate possibilities of how things could unfold.
• Refuses to self-reflect about how they’ve arrived to their current position.
• Ignores the past and future in favor of the present moment.
• Expects others to take ownership and power over situations.
• Refuses to pick a direction in life.
• Avoids imagining potentials, possibilities, and future desires.
• Overwhelmed by thinking about cause and effect.
• Wants others to offer up observations of the past and projected future.
• Ignores themes and power dynamics.
• Depends on others to identify obstacles in their way.
• Feels stifled by being forced to process all the ways in which something could evolve.
4L: Disowned Logic
The 4L attitude is characterized by a self-negative (Ls-) and others-positive (Lo+) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that disowns how the realm of logic may affect them. 4Ls come to an understanding that outside sources have a better grasp over the aspect. The 4L feels a sense of carelessness with generating its own logic, and generally desires quick conclusions when they are forced to produce opinions in this realm. The strategies that each 4L employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of acceptance of outside opinions regarding logical reasoning will be consistent and true for all 4Ls. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 4Ls. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 4L attitude.
• Expects others to give detailed reasons about how things work.
• Disinterested in proving what is true or false.
• Detaches from choosing things based on correctness in favor of going with what they like.
• Depends on others to make sense of new information.
• Ignores organizing detailed information.
• Refuses to create systems and rules for themselves.
• Rarely interested in continuously probing “why” something works.
• Overwhelmed by reiterating complex details and reasons.
• Refuses to process out how they arrived to their conclusions.
• Wants others to debrief them on what decisions were made.
• Expects to be given an overview of how things operate.
• Depends on others to correct them if they’re wrong rather than expecting self-correction.
4F: Disowned Physics
The 4F attitude is characterized by a self-negative (Fs-) and others-positive (Fo+) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that disowns how the realm of physics may affect them. 4Fs come to an understanding that outside sources have a better grasp over the aspect. The 4F feels a sense of carelessness with generating its own perceptions of the physical world, and generally desires quick conclusions when they are forced to produce opinions in this realm. The strategies that each 4F employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of acceptance of outside responsibility of the physical and sensual world will be consistent and true for all 4Fs. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 4Fs. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 4F attitude.
• Unattached to the physical world around them and how it makes them feel.
• Has an unconcerned attitude about paying attention to own comfort levels and bodily sensations.
• Ignores opportunities to better their living environment.
• Forgets to check in with their current feelings and emotions.
• Disowns caring about how their environment keeps them inefficient.
• Tends to forget to track what’s comfortable.
• Hoists responsibility to manage environments onto others.
• Ignores their own senses and feelings.
• Forgets to schedule doctor check-ups, maintenance, meetings and follow-ups.
• Detaches from the senses in favor of intuitive ideas.
• Downplays feelings and moods.
• Becomes exhausted by updating wardrobe, health routines, and daily necessities.
• Loses track of objects or forgets to operate things consistently.
4E: Disowned Expression
The 4E attitude is characterized by a self-negative (Es-) and others-positive (Eo+) disposition. This disposition creates an attitude that disowns how the realm of expression may affect them. 4Es come to an understanding that outside sources have a better grasp over the aspect. The 4E feels a sense of carelessness with generating personal judgments, and generally desires quick conclusions when they are forced to produce opinions in this realm. The strategies that each 4E employs may differ in behavior or execution but the core attitude of acceptance of outside opinions regarding expression will be consistent and true for all 4Es. Below are some common beliefs and behaviors that you may see with 4Es. Please keep in mind that these are generalities and do not represent the vast sub-archetypes held within the overall 4E attitude.
• Refuses to personally judge others unless there’s objective reasoning available to share.
• Unsure of who they like or dislike on a gut level.
• Ignores deciding the meaning and personal significance of those around them.
• Doubts whether their affinity towards people is valuable enough to accept.
• Disowns their likes and dislikes
• Refuses to come up with judgments of why some people are better than others.
• Wants others to verbalize why they like or dislike them.
• Judgements are doled out based on merit rather than subjective reasons.
• Doesn’t recognize their biases towards certain people.
• Expects others to mind-read the 4E’s likes and dislikes.
• Fears being forced to unveil their personal evaluations of people’s worth.
Subtypes
The subtypes in Attitudinal Psyche are patterns of focus on specific sub-attitudes that make up the attitudes. These subtypes manifest in behavior mainly through verbal communication, and can be best observed during extended conversation.
– Depth subtypes dig deeper by quickly rifling through the personal attitude valences (Xs+/Xs-, Xo+/Xo-).
– Self-focused subtypes overdo the self-positive or self-negative attitude valences (Xs+/Xs-).
– Others-focused subtypes overdo the others-positive or others-negative attitude valences (Xo+/Xo-).
– Method-focused subtypes overdo the impersonal attitude valences (Xr/Xp).
– Adaptation/obscuring-focused subtypes hide the personal attitude valences (Xs+/Xs-, Xo+/Xo-).
Behavioral Patterns of the Subtypes in Conversation
Depth Subtypes (1-1, 2-2, 3-3, 4-4):
– Switches quickly between self and others perspectives
– Goes in depth, explores all angles, finds more things to say from every vantage point
– Explain things further, responds well to more interest
– Has a lack of hiding, obscuring, or distracting in communication
– Bold and vulnerable in communicating their true opinions
Self-Focused Subtypes (1-2, 2-1, 3-4, 4-3):
– Self-centered, self-absorbed, prefers to shift conversations towards their own experiences
– Monologues and references past monologues to build the narrative
– Communicates their internal reactions to things
– Autobiographical
– Haughty and opinionated; magnifies their own perspective
Others-Focused Subtypes (1-3, 2-4, 3-1, 4-2):
– Over-involves themselves in other people’s opinions and reactions
– Listens, nit-picks, wonders, corrects, questions, and becomes intertwined with others
– Quickly changes and adjusts based on how others react
– Pries, draws attention to, and indulges in the reactions of others
– Catalogs information based on who it comes from
Method-Focused Subtypes (1-4, 2-3, 3-2, 4-1):
– Remains impersonal and detached from reactions taking place
– Picky about information and details surrounding the aspect
– Has other overarching motives unrelated to the conversation at hand
– Becomes blind to overt personal relating and individualizing when communicating
– Talks about the structure and framework of things rather than the affects they have on people
Adaptation/Obscuring (Zero) Subtypes (1-0, 2-0, 3-0, 4-0)
– Adapts to others in conversation
– Hides, suppresses, or dismisses overly penetrating questions
– Talks about universal, similar, and relatable experiences that feel “safe”
– Dampens their own reactions to others; underexaggerates how others reacted when retelling events
– Avoids giving away too many indications of their true opinions
Subtypes Cheat-sheet
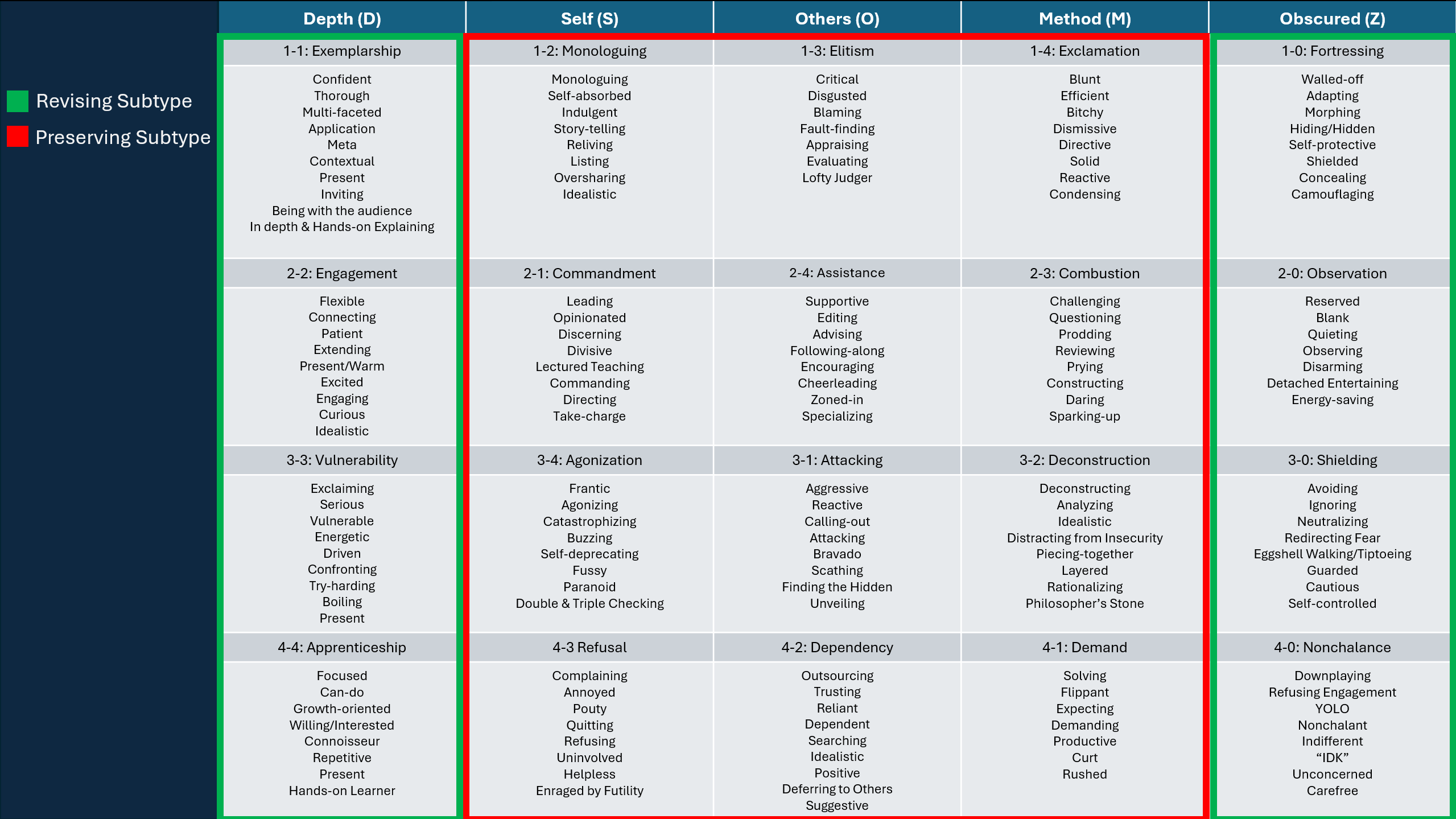
This subtype cheat-sheet is a screen capture from TTV Theory Ep: Subtypes – Massive Overhaul. For more exclusive information View The Episode Here.
To learn about “Revising” versus “Preserving” subtypes, check out TTV Theory Episode View The Episode Here.
