Assistance
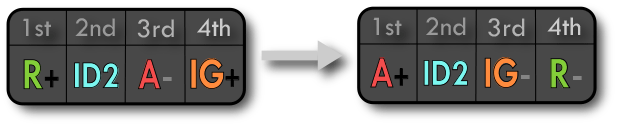
Relationships of Assistance involve both types discussing and helping each other through life. The Assistant in this relation often takes the role of decision maker, making sure that the Assistee is correctly applying themselves. This relation generally does not evolve into groups, however, all three types in this relation may come together to check and edit one another’s work, often pointing out blind spots. The Assistant relation is the most compatible out of the Triangular relations, as the shared second aspect ensures that communication is always open regarding that aspect. This has an uplifting and mitigating effect on any other negative positionings of the attitude relations, which is also why the Identical2 relation is ranked as the highest out of all the Identical Attitude relations.
The Assistant monitors the oblivious needs of the Assistee and corrects issues whenever possible. The first aspect of the Assistant pairs with the fourth aspect of the Assistee, which allows the Assistee to trust their partner to handle the details of this area of life. When there is confusion over this result aspect, the partners can simply clarify misunderstandings through discussion of the second aspect. Both aspects work in tandem, so if any part of reality incorporates both, the pairing will flourish. Partners share the flexible aspect in this relation, which is a common anchor point to handle any conflicts. The synergy between the result aspects and the flexible aspects ensure that individuals stay useful and enjoyable to each other in the relationship.
The Assistance relation is asymmetrical among members. While part of their results relationship has synergy, the Assistee’s dominant aspect conflicts with the same insecure aspect as the Assistant. The Assistant is confident about correcting matters of their first aspect although their efforts are sometimes scrutinized by the Assistee. It is common for the Assistant to at first feel resentful of their partner’s pressure to focus on what they are not ready to address. However, the Assistant enjoys discussing any points they are unsure about with their partner through their shared flexible aspect. While the Assistee can be impatient with their partner’s hesitancy in their confident area, they appreciate all the Assistant’s help with the area of life they do not independently attend to. This relation is the most likely catalyst for the Assistant to understand and accept how they must improve the results of their insecure aspect. It has the power to fully help both parties individuate. There is some evidence that this relationship is the most common between romantic partners in the world.
There is a shared weak point in relationships of Assistance. The Assistant does not attend to the area of life that the Assistee is insecure about. At times, the Assistee feels that their deep insecurities and any attempts to process them are ignored by the Assistant. If the Assistee is sufficiently ungrounded in their insecurities, they may blame their partner for overlooking their needs or resort to their dominant aspect to inflict a similar feeling to the insecurity of their partner. The Assistant believes they are unequipped to process their partner’s insecurities and often communicates through the flexible aspect to understand their viewpoint. The ignored area of life in relationships of Assistance allows the Assistant to gain sensitivity to their oblivious aspect and allows the Assistee to recognize imagined threats. It is quite resilient how the second aspect minimizes negativity.
Pair Chains
Types are only repeated to show that the chain continues and each type has a pairing on each side. The repeated type is not significant.